359 字
2 分钟
Spring之ApplicationContext的继承关系影响AOP增强实现
参考链接
[Core Technologies——Spring ](https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/5.2.6.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/core.html#spring-core)Spring之ApplicationContext的继承关系影响AOP增强实现
以两个ApplicatonContext类的关系为例
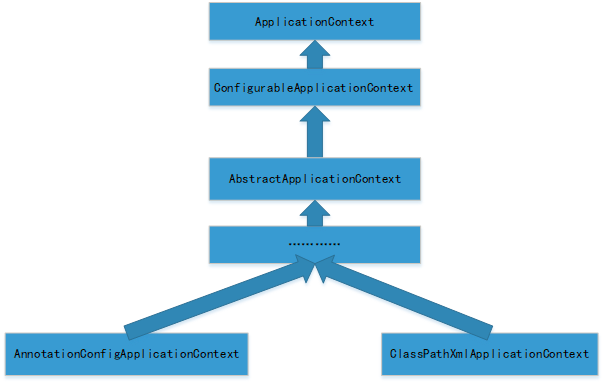也可以简单理解为注解式的ApplicationContext与xml式的Application Context的区别,因为也有两种实现AOP增强的方式,要注意的是java配置的AOP拦截,是不会拦截到xml中配置中bean的,除非在xml中配置<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
注解设置AOP增强
@Aspect@Slf4jpublic class FooAspect { @AfterReturning("bean(testBean*)") public void printAfter() { log.info("after hello()"); }}xml设置AOP增强,在ApplicationContext.xml中增加 <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> 允许AOP增强。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
<bean id="testBeanX" class="geektime.spring.web.context.TestBean"> <constructor-arg name="context" value="Bar" /> </bean>
</beans>运行测试
TestBean.java
```java @AllArgsConstructor @Slf4j public class TestBean { private String context;public void hello() { log.info("hello " + context);}}
<h4 id="1mO4r">FooAspect.java</h4>```javapackage geektime.spring.web.foo;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
@Aspect@Slf4jpublic class FooAspect { @AfterReturning("bean(testBean*)") public void printAfter() { log.info("after hello()"); }}FooConfig
```java package geektime.spring.web.foo;import geektime.spring.web.context.TestBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
@Configuration @EnableAspectJAutoProxy public class FooConfig { @Bean public TestBean testBeanX() { return new TestBean(“foo”); }
@Beanpublic TestBean testBeanY() { return new TestBean("foo");}
@Beanpublic FooAspect fooAspect() { return new FooAspect();}}
<h4 id="T0LIi">applicationContext.xml</h4>```xml<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
<bean id="testBeanX" class="geektime.spring.web.context.TestBean"> <constructor-arg name="context" value="Bar" /> </bean>
<!-- <bean id="fooAspect" class="geektime.spring.web.foo.FooAspect" />--></beans>ContextHierarchyDemoApplication.java
```java @SpringBootApplication @Slf4j public class ContextHierarchyDemoApplication implements ApplicationRunner {public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ContextHierarchyDemoApplication.class, args);}
@Overridepublic void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception { ApplicationContext fooContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(FooConfig.class); ClassPathXmlApplicationContext barContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( new String[] {"applicationContext.xml"}, fooContext); TestBean bean = fooContext.getBean("testBeanX", TestBean.class); bean.hello();
log.info("=============");
bean = barContext.getBean("testBeanX", TestBean.class); bean.hello();
bean = barContext.getBean("testBeanY", TestBean.class); bean.hello();}}
Spring之ApplicationContext的继承关系影响AOP增强实现
https://iszengmh.pages.dev/posts/spring之applicationcontext的继承关系影响aop增强实现/